# init repo notebook
!git clone https://github.com/rramosp/ppdl.git > /dev/null 2> /dev/null
!mv -n ppdl/content/init.py ppdl/content/local . 2> /dev/null
!pip install -r ppdl/content/requirements.txt > /dev/null
Learnable parameters#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
from scipy.integrate import quad
from progressbar import progressbar as pbar
from rlxutils import subplots, copy_func
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
tfd = tfp.distributions
tfb = tfp.bijectors
%matplotlib inline
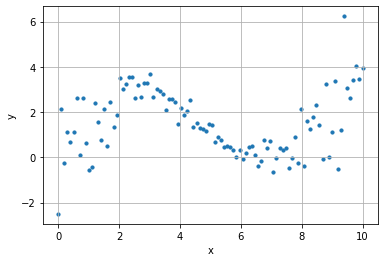
n_points = 100
k = 2
x = np.linspace(0, 10, n_points)
y = .3*x+2*np.sin(x/1.5) + (.2+.02* ((x-5)*k)**2) * np.random.randn(n_points)
plt.scatter(x, y, s=10)
plt.grid();
plt.xlabel("x"); plt.ylabel("y")
Text(0, 0.5, 'y')
inp = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(1,))
out = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="tanh")(inp)
out = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="tanh")(out)
out = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2)(out)
out = tfp.layers.IndependentNormal()(out)
m = tf.keras.models.Model(inp, out)
m.summary()
Model: "model_2"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_3 (InputLayer) [(None, 1)] 0
dense_6 (Dense) (None, 10) 20
dense_7 (Dense) (None, 10) 110
dense_8 (Dense) (None, 2) 22
independent_normal_2 (Indep ((None,), 0
endentNormal) (None,))
=================================================================
Total params: 152
Trainable params: 152
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
negloglik = lambda x, distribution: -distribution.log_prob(x)
m.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=negloglik)
history = m.fit(x,y, epochs=2000, verbose=0)
plt.plot(history.epoch, history.history['loss'])
plt.grid(); plt.xlabel("epoch"); plt.ylabel("loss");
get the predictive distributions for each input data point
_y = m(x)
_y
<tfp.distributions._TensorCoercible 'tensor_coercible' batch_shape=[100] event_shape=[] dtype=float32>
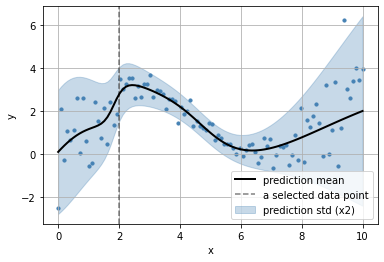
observe the parameters learn for each datapoint
_x = np.r_[2]
_x
array([2])
loc = _y.parameters['distribution'].parameters['loc'].numpy()
scale = _y.parameters['distribution'].parameters['scale'].numpy()
plt.scatter(x, y, s=10, color="steelblue")
plt.plot(x, loc, color="black", lw=2, label="prediction mean")
plt.fill_between(x,
loc + 2*scale,
loc - 2*scale, alpha=.3,
color="steelblue",
label="prediction std (x2)")
plt.axvline(_x[0], color="black", ls="--", alpha=.5, label="a selected data point")
plt.grid(); plt.legend();
plt.xlabel("x"); plt.ylabel("y")
Text(0, 0.5, 'y')
we can also see how it generalizes outside the input variable bounds
xr = np.linspace(np.min(x)-10, np.max(x)+10, 100)
yr = m(xr)
loc = yr.parameters['distribution'].parameters['loc'].numpy()
scale = yr.parameters['distribution'].parameters['scale'].numpy()
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
plt.scatter(x, y, s=10, color="steelblue")
plt.plot(xr, loc, color="black", lw=2, label="prediction mean")
plt.fill_between(xr,
loc + 2*scale,
loc - 2*scale, alpha=.3,
color="steelblue",
label="prediction std (x2)")
plt.axvline(_x[0], color="black", ls="--", alpha=.5, label="a selected data point")
plt.grid(); plt.legend();
plt.xlabel("x"); plt.ylabel("y")
Text(0, 0.5, 'y')
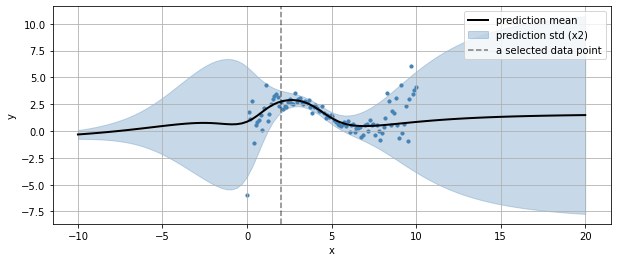
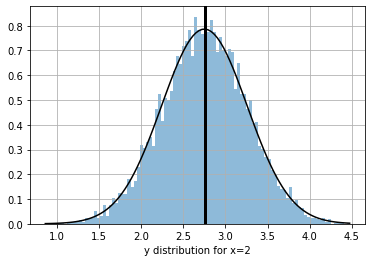
we can get the predictive distribution of any input data point (such as the selected one above)
_xd = m(_x)
_xd
<tfp.distributions._TensorCoercible 'tensor_coercible' batch_shape=[1] event_shape=[] dtype=float32>
_ys = _xd.sample(10000)[:,0].numpy()
_yr = np.linspace(np.min(_ys), np.max(_ys), 100)
plt.plot(_yr, np.exp(_xd.log_prob(_yr)), color="black", alpha=1)
plt.hist(_ys, bins=100, density=True, alpha=.5);
plt.axvline(_ys.mean(), color="black", lw=3)
plt.grid(); plt.xlabel(f"y distribution for x={_x[0]}")
Text(0.5, 0, 'y distribution for x=2')
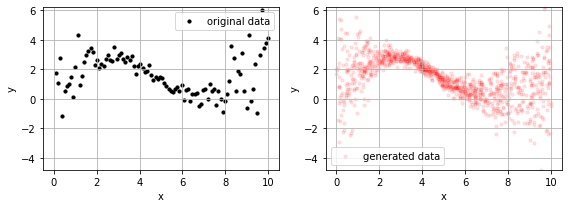
and, since we have distributions we also have a generative model using the .predict method for sampling.
_x = np.random.random(1000)*(np.max(x)-np.min(x)) + np.min(x)
_y = m.predict(_x)
for ax,i in subplots(2, usizex=4):
if i==1: plt.scatter(_x, _y, s=10, alpha=.1, color="red", label="generated data");
if i==0: plt.scatter(x, y, s=10, alpha=1, color="black", label="original data")
plt.grid(); plt.legend();
plt.xlabel("x"); plt.ylabel("y")
plt.ylim(np.min(_y), np.max(_y))
plt.tight_layout()